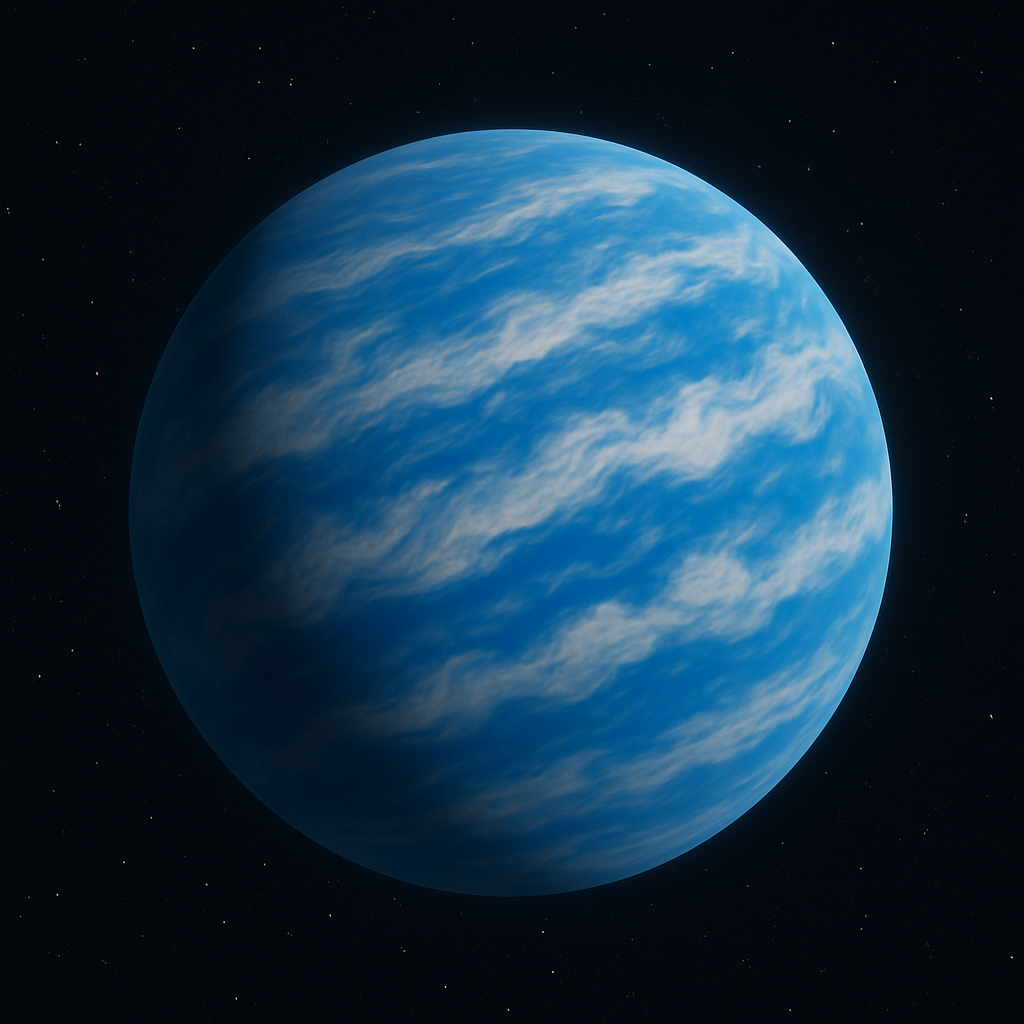
Zeus
Page Under Construction (Update November 2025) |
|---|
This gas giant migrated inward, likely due to planetary shuffling as this star system formed eons ago. Due to extensive water vapor clouds, the gas giant is subject to a strong greenhouse effect (offsetting its increased albedo), which in addition to heat from the core, raise the temperature some 100 degrees above its equilibrium temperature of -59C.
The planet has three large moons, one of them a carbon moon (like Saturn's moon, Titan). Since the mass of Zeus is between that of Saturn and Neptune, it is conjectured that the large moons Zeus now has were captured as the planet migrated inward. This would have caused many of its native moons to be ejected, leading to the small population of moons today.
Planet Properties
- Classification: Water Jovian World
- Orbital Distance: 0.50 AU
- Surface Temperature: +41C
- Axial Tilt: 3.2°
- Year⊕: 144 days, 8 hours, 33 minutes, 8 seconds
- Day⊕: 14 hours 22 minutes
- Mass⊕: 28 Earths (Between Saturn and Neptune)
- Radius⊕: 4.2 Earths
- Escape Velocity: 28.88 km/s
- Magnetosphere: Strong
- Radiation: High (Ultraviolet)
- Satellites: 9 (Olympia, Demeter, Apollo)
- Population:
Tau Ceti II
Related Articles
The Tau Ceti Star SystemHistory of the Tau Ceti Star System
Monopolium
Moons
Tau Ceti II-1: OlympiaTau Ceti II-2: Demeter
Tau Ceti II-8: Apollo